Table of contents
- ✨Python Data Types
- ✨Data Structures
- ✨Task-1: Give the Difference between List, Tuple and set. Do Hands-on and put screenshots as per your understanding.
- ✨Task-2: Create below Dictionary and use Dictionary methods to print your favorite tool just by using the keys of the Dictionary.
- ✨Task-3: Create a List of cloud service providers eg. cloud_providers = ["AWS","GCP","Azure"] & Write a program to add Digital Ocean to the list of cloud_providers and sort the list in alphabetical order.
- ✨Conclusion
✨Python Data Types
Data types are the classification or categorization of data items. It represents the kind of value that tells what operations can be performed on a particular data. Since everything is an object in Python programming, data types are actually classes and variables are instance (object) of these classes. Python has the following data types built-in by default: Numeric(Integer, complex, float), Sequential(string, lists, tuples), Boolean, Set, Dictionaries, etc.
To check what is the data type of the variable used, we can simply write:
# Define some variables
integer_var = 42
float_var = 3.14
string_var = "Hello, world!"
list_var = [1, 2, 3]
tuple_var = (1, 2, 3)
dict_var = {"key": "value"}
boolean_var = True
none_var = None
# Check the data type of each variable
print(type(integer_var)) # Output: <class 'int'>
print(type(float_var)) # Output: <class 'float'>
print(type(string_var)) # Output: <class 'str'>
print(type(list_var)) # Output: <class 'list'>
print(type(tuple_var)) # Output: <class 'tuple'>
print(type(dict_var)) # Output: <class 'dict'>
print(type(boolean_var)) # Output: <class 'bool'>
print(type(none_var)) # Output: <class 'NoneType'>
✨Data Structures
In Python, a data structure is a way of organizing and storing data in a particular format so that it can be accessed and manipulated efficiently. Python offers several built-in data structures, each with its own characteristics and use cases. Here's an overview of some commonly used data structures in Python:
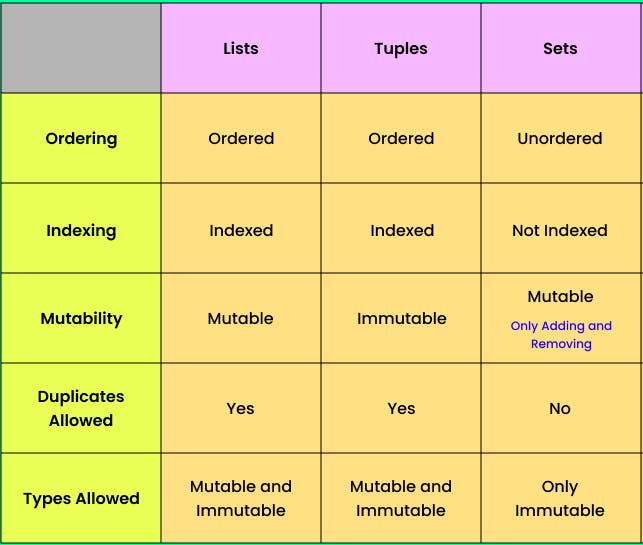
Lists:
Ordered collection of items.
Mutable (can be modified after creation).
Allows duplicate elements.
Accessed by index.
Syntax:
[item1, item2, ...].
Tuples:
Ordered collection of items.
Immutable (cannot be modified after creation).
Allows duplicate elements.
Accessed by index.
Syntax:
(item1, item2, ...).
Sets:
Unordered collection of unique items.
Mutable (can be modified after creation).
Does not allow duplicate elements.
Does not support indexing.
Syntax:
{item1, item2, ...}.
Dictionaries:
Collection of key-value pairs.
Mutable (can be modified after creation).
Keys are unique and immutable (e.g., strings, numbers, tuples).
Values can be of any data type.
Accessed by key.
Syntax:
{key1: value1, key2: value2, ...}.
Strings:
Sequence of characters.
Immutable (cannot be modified after creation).
Accessed by index.
Syntax:
'string'or"string".
Arrays (from
arraymodule):Similar to lists but homogeneous (all elements must be of the same type).
More memory efficient compared to lists for certain use cases.
Stacks and Queues (can be implemented using lists or deque):
Stacks follow Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle.
Queues follow First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle.
Heaps (from
heapqmodule):Binary tree-based data structure.
Efficiently maintains a partially ordered tree.
Useful for implementing priority queues.
Linked Lists:
Consists of nodes where each node points to the next node in the sequence.
Different from lists in Python; often implemented manually or using third-party libraries.
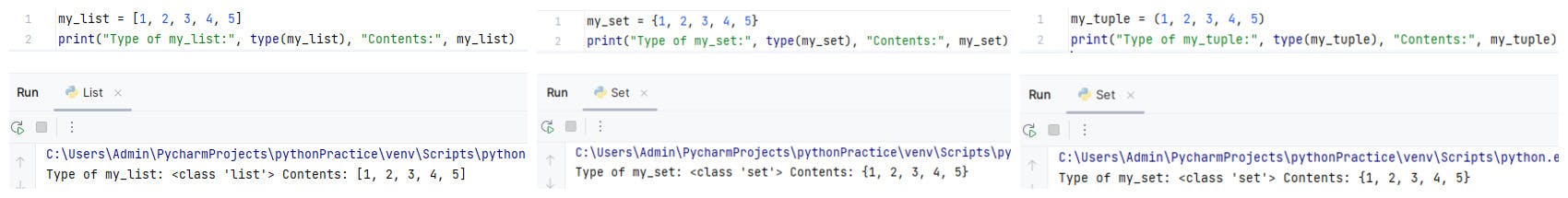
✨Task-1: Give the Difference between List, Tuple and set. Do Hands-on and put screenshots as per your understanding.
Examples of List, Set & Tuple:
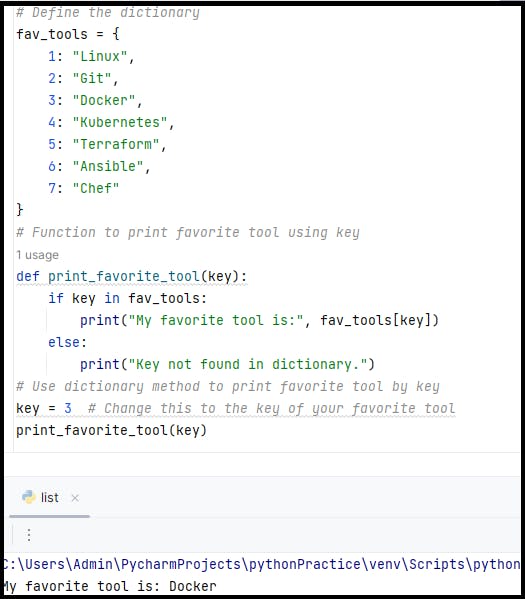
✨Task-2: Create below Dictionary and use Dictionary methods to print your favorite tool just by using the keys of the Dictionary.
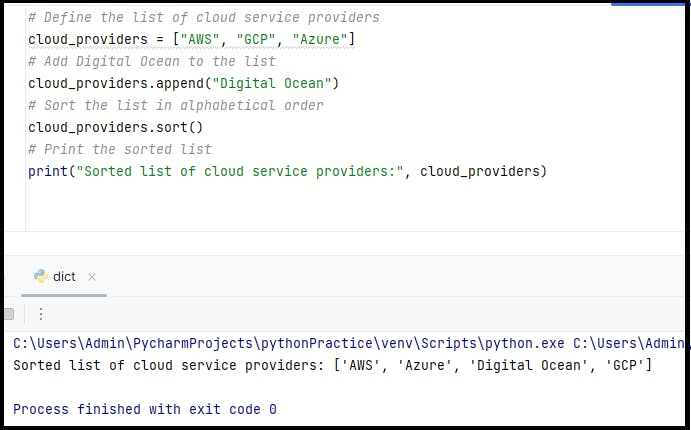
✨Task-3: Create a List of cloud service providers eg. cloud_providers = ["AWS","GCP","Azure"] & Write a program to add Digital Ocean to the list of cloud_providers and sort the list in alphabetical order.
✨Conclusion
Python's versatile data types and data structures empower DevOps practitioners with efficient tools for managing and manipulating data, enhancing productivity and facilitating streamlined development processes in diverse operational contexts.
I believe this blog will be really helpful, giving you fresh perspectives and teaching you something new and interesting. 🙏
😊 Enjoy learning!